颜色
来自Labplus盛思维基百科
概述
基于不同颜色物体对于RGB光线反射率不同的原理来分辨物体的颜色RGB分量。采用I2C通讯,操作简单,直接输出被测物体RGB分量值。
技术参数
- 工作电压:VCC 3.3-5V
- 接口方式:I2C接口
- 模块尺寸:24x46x7.5mm
引脚定义
| VCC | 电源 |
| SDA | I2C数据 |
| SCL | I2C时钟 |
| GND | 地 |
使用教程
在使用时被测物体须要置于颜色传感器1CM处,使其能反射光线。要注意环境光线对颜色测量影响,最好在密闭的黑暗环境下测量。
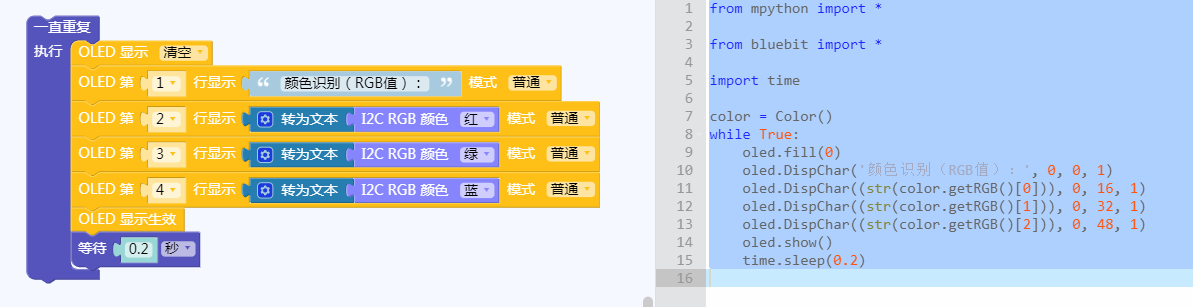
掌控板及mPython编程
#程序功能:用掌控板OLED屏显示颜色传感器检测的RGB颜色分量。
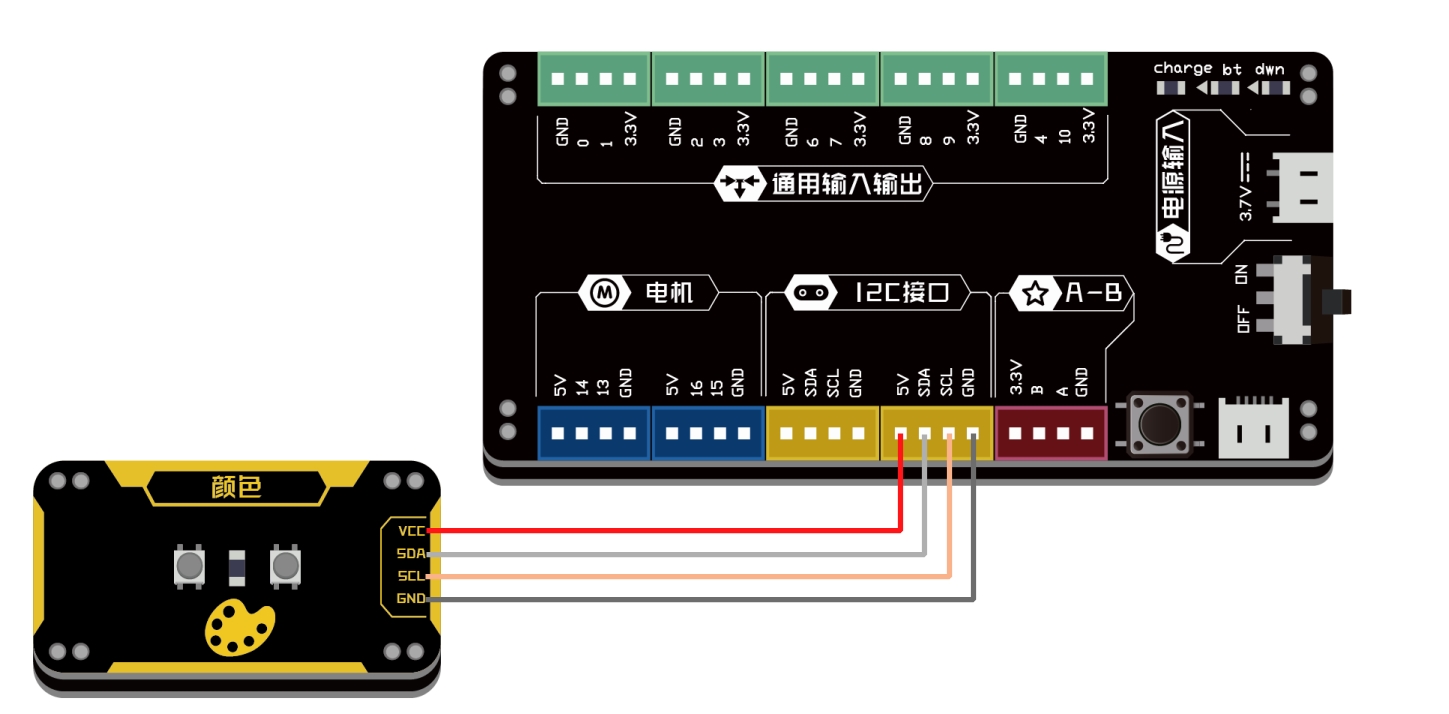
| 连接示意图 |
| 图形化及mPython代码 |
Arduino示例
//程序功能:识别物体的颜色,以R、G、B形式打印出来//
#include <Wire.h>
#include "colorRecognition.h"
uint8_t r, g, b;
float scaleR,scaleG, scaleB;
extern ColorRecognitionClass ColorRecognition;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
ColorRecognition.begin(); //wire 初始化
}
void loop()
{
ColorRecognition.startConvert(); //wire开始传输
delay(100);
if (ColorRecognition.getStatus()) //获取ColorRecognition状态,返回true正常,false异常
{
ColorRecognition.getRGB(r, g, b); //获取颜色传感器的rgb值
}
Serial.print("g: "); Serial.print(g);
Serial.print(" b: "); Serial.print(b);
Serial.print(" r: "); Serial.print(r);
Serial.println("");
}
Bluebit主控
连接示意图
from microbit import *
import math
def getColor():
color = [0, 0, 0]
i2c.write(0x0a, bytearray([1]))
sleep(100)
i2c.write(0x0a, bytearray([2]))
state = i2c.read(0x0a, 1)
if state[0] == 3:
i2c.write(0x0a, bytearray([3]))
c = i2c.read(0x0a, 6)
color[0] = c[5]*256+c[4] # color R
color[1] = c[1]*256+c[0] # color G
color[2] = c[3]*256+c[2] # color B
maxColor = max(color[0], color[1], color[2])
if maxColor > 255:
scale = 255/maxColor
color[0] = int(color[0]*scale)
color[1] = int(color[1]*scale)
color[2] = int(color[2]*scale)
return color
while True:
c = getColor() # 返回3字节依次为RGB值
print("R: %d, G: %d, B: %d" % (c[0], c[1], c[2]))
sleep(200)
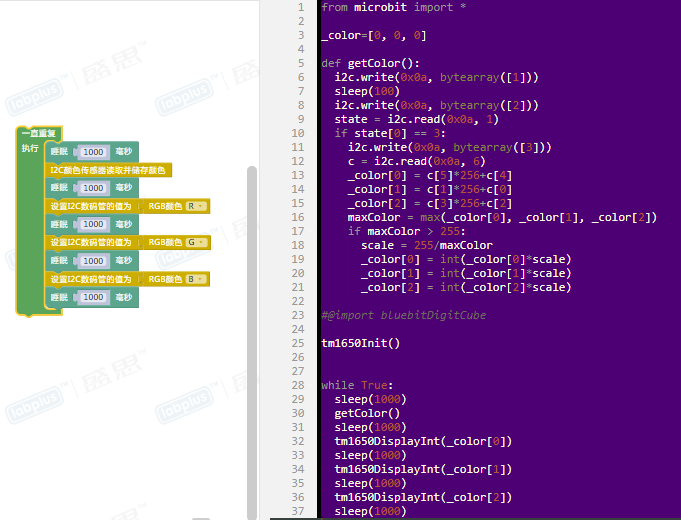
图形化示例
程序功能:用数码管分别显示颜色传感器测出的颜色的R、G、B的数值
版本历史记录
| Version | Date | Note [+]新增[-]删除[^]修复 |
|---|---|---|
| V2.0 |