“Game:bit”的版本间的差异
来自Labplus盛思维基百科
Tangliufeng(讨论 | 贡献) |
Huanglanying(讨论 | 贡献) (震动马达:Pin16 => pin16) |
||
| (未显示2个用户的22个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| + | [[文件:游戏手柄-01.png|450px|缩略图|右]] | ||
== 概述 == | == 概述 == | ||
microbit拓展游戏手柄。拥有丰富的输入按键、双轴游戏摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器。结合microbit可以有多样的玩法,增加microbit编程的趣味性! | microbit拓展游戏手柄。拥有丰富的输入按键、双轴游戏摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器。结合microbit可以有多样的玩法,增加microbit编程的趣味性! | ||
== 技术参数 == | == 技术参数 == | ||
| − | * | + | * 输入电源:3V(2节7号干电池) |
* PCI插槽可插入microbit作主控 | * PCI插槽可插入microbit作主控 | ||
* 拥有丰富的按键、双轴摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器 | * 拥有丰富的按键、双轴摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== 使用教程 == | == 使用教程 == | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! style="background:#7dc2f5"| | + | ! style="background:#7dc2f5"|game:bit |
! style="background:#7dc2f5"|说明 | ! style="background:#7dc2f5"|说明 | ||
! style="background:#7dc2f5"|micro:bit引脚 | ! style="background:#7dc2f5"|micro:bit引脚 | ||
! style="background:#7dc2f5"|Python示例 | ! style="background:#7dc2f5"|Python示例 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 双轴按键游戏摇杆 ||三路模拟输出, | + | | 双轴按键游戏摇杆 ||三路模拟输出,输出值分别对应(X,Y)双轴偏移量和Z轴;<br />按下的输出模拟量800~850,松开输出模拟量1023|| X轴->P2<br /> Y轴->P1<br />Z按键->P0 || 获取x轴偏移量: pin2.read_analog()<br />获取z按键模拟量: pin0.read_analog() |
|- | |- | ||
| 第25行: | 第23行: | ||
当B按下按键输出模拟量400~450, 松开输出模拟量1023<br /> | 当B按下按键输出模拟量400~450, 松开输出模拟量1023<br /> | ||
当A按下按键输出模拟量600~650, 松开输出模拟量1023 | 当A按下按键输出模拟量600~650, 松开输出模拟量1023 | ||
| − | || | + | || P0 || pin0.read_analog() |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 「START」按键 || 「START」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_A,功能与microbit的A按键功能相同 || BUTTON_A( | + | | 「START」按键 || 「START」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_A,功能与microbit的A按键功能相同 || BUTTON_A(P5) || button_a.is_pressed()==True #当「START」按键按下 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 「SElECT」按键 ||「SElECT」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_B,功能与microbit的B按键功能相同 || BUTTON_B( | + | | 「SElECT」按键 ||「SElECT」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_B,功能与microbit的B按键功能相同 || BUTTON_B(P11) || button_b.is_pressed()==True #当「SELECT」按键按下 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 震动马达 || 输入高电平,触发震动马达,低电平停止震动 || | + | | 震动马达 || 输入高电平,触发震动马达,低电平停止震动 || P16 || pin16.write_digital(1) #震动开启<br />pin16.write_digital(0) #停止震动 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 无源蜂鸣器 || 设置频率或音阶,可发出对应频率的电子声音 || | + | | 无源蜂鸣器 || 设置频率或音阶,可发出对应频率的电子声音 || P8 || music.pitch(1000,1000,pin8) #蜂鸣器发出1KHz,持续1秒的声音 |
|} | |} | ||
| − | === < | + | |
| + | == 应用示例 == | ||
| + | === <big>无线遥控器</big> === | ||
| + | 可利用microbit的无线功能,发送game:bit的按键数据。另外一块microbit接收数据后,作出响应。达到无线遥控的功能。可应用在无线遥控手柄的场景上。<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <big>game:bit & micro:bit发送端程序:</big><br /> | ||
| + | [http://wiki.labplus.cn/images/6/6c/Gamebit_wireless_remote.zip game:bit无线遥控例程下载] | ||
| + | <pre style="color:blue"> | ||
| + | from microbit import * | ||
| + | import radio | ||
| + | |||
| + | def getKeyVal(): | ||
| + | key = 0 | ||
| + | btVal = pin0.read_analog() | ||
| + | if (btVal < 70): | ||
| + | key = 1 # button Y | ||
| + | elif (btVal < 270 and btVal > 130): | ||
| + | key = 2 # button X | ||
| + | elif (btVal < 470 and btVal > 330): | ||
| + | key = 3 # button B | ||
| + | elif (btVal < 670 and btVal > 530): | ||
| + | key = 4 # button A | ||
| + | elif (btVal < 870 and btVal > 730): | ||
| + | key = 5 # rocker button | ||
| + | if button_a.is_pressed(): | ||
| + | key = 6 # button start | ||
| + | if button_b.is_pressed(): | ||
| + | key = 7 # button select | ||
| + | return key | ||
| + | |||
| + | radio.config(length=32, queue=3, channel=7, power=0, data_rate=radio.RATE_1MBIT) | ||
| + | radio.on() | ||
| + | while True: | ||
| + | sendBuff = [0,0,0,0,0,0] | ||
| + | tmp = pin2.read_analog() # axix x | ||
| + | sendBuff[0] = tmp & 0xff | ||
| + | sendBuff[1] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff | ||
| + | tmp = pin1.read_analog() # axis y | ||
| + | sendBuff[2] = tmp & 0xff | ||
| + | sendBuff[3] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff | ||
| + | tmp = getKeyVal() # button val | ||
| + | sendBuff[4] = tmp & 0xff | ||
| + | sendBuff[5] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff | ||
| + | radio.send_bytes(bytearray(sendBuff)) | ||
| + | #print(sendBuff) | ||
| + | sleep(50) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <big>micro:bit接收端程序:</big><br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre style="color:blue"> | ||
| + | from microbit import * | ||
| + | import radio | ||
| + | |||
| + | radio.config(length=32, queue=3, channel=7, power=0, data_rate=radio.RATE_1MBIT) | ||
| + | radio.on() | ||
| + | while True: | ||
| + | tmp = radio.receive_bytes() | ||
| + | if (tmp != None): | ||
| + | x = (tmp[1]<<8)|tmp[0] | ||
| + | y = (tmp[3]<<8)|tmp[2] | ||
| + | key = (tmp[5]<<8)|tmp[4] | ||
| + | #print(x) | ||
| + | #print(y) | ||
| + | #print(key) | ||
| + | </pre><br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === <big>走迷宫</big> === | ||
| + | game:bit手柄和micro:bit的led屏互动的小游戏!通过game:bit的摇杆控制来行走迷宫,趣味十足!<br /><br /> | ||
| + | [http://wiki.labplus.cn/images/e/ed/Gamebit_%E8%B5%B0%E8%BF%B7%E5%AE%AB.zip gamebit_maze例程下载] | ||
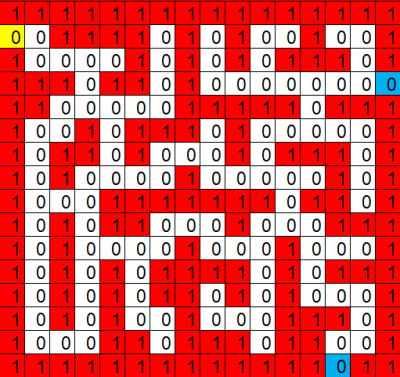
| + | * 以下迷宫图,从黄色点启始,蓝色点为出口。也可通过修改maze[]数组,设计自己的迷宫图! | ||
| + | [[文件:Gamebit maze.png|400px|border]] | ||
<pre style="color:blue"> | <pre style="color:blue"> | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | A simple maze program. You are the flashing dot and can walk around | ||
| + | using the accelerometer. | ||
| + | """ | ||
| + | |||
| + | import microbit | ||
| + | from microbit import * | ||
| + | import music | ||
| + | |||
| + | d = microbit.display | ||
| + | |||
| + | # the maze data, as binary numbers (outside walls are added automatically) | ||
| + | maze = [ | ||
| + | 0b1111111111111111, | ||
| + | 0b0011110101001001, | ||
| + | 0b1000010101011101, | ||
| + | 0b1110110100000000, | ||
| + | 0b1100000111110111, | ||
| + | 0b1001011101000001, | ||
| + | 0b1011010001011101, | ||
| + | 0b1010000100000101, | ||
| + | 0b1000111111101101, | ||
| + | 0b1010110001000111, | ||
| + | 0b1010000100010001, | ||
| + | 0b1010101111010111, | ||
| + | 0b1010101101010001, | ||
| + | 0b1010100100011101, | ||
| + | 0b1000110111011001, | ||
| + | 0b1111111111111011, | ||
| + | ] | ||
| + | def getRockerVal(): | ||
| + | Dir = 0 | ||
| + | val1 = pin1.read_analog() | ||
| + | val2 = pin2.read_analog() | ||
| + | if val1 > 750: | ||
| + | Dir = 1 #up | ||
| + | elif val1 < 250: | ||
| + | Dir = 2 #down | ||
| + | elif val2 < 250: | ||
| + | Dir = 3 #left | ||
| + | elif val2 > 750: | ||
| + | Dir = 4 #right | ||
| + | print(Dir) | ||
| + | return Dir | ||
| + | |||
| + | def get_maze(x, y): | ||
| + | if 0 <= x < 16 and 0 <= y < 16: | ||
| + | return (maze[y] >> (15 - x)) & 1 | ||
| + | else: | ||
| + | return 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | def draw(x, y, tick): | ||
| + | img = microbit.Image(5,5) | ||
| + | for j in range(5): | ||
| + | for i in range(5): | ||
| + | img.set_pixel(i, j, get_maze(x + i - 2, y + j - 2)*5) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # draw the player, flashing | ||
| + | img.set_pixel(2, 2, (tick & 1)*4+5) | ||
| + | d.show(img) | ||
| + | |||
| + | def main(): | ||
| + | x = 0 | ||
| + | y = 1 | ||
| + | tick = 0 | ||
| + | while True: | ||
| + | dir = getRockerVal() | ||
| + | tick += 1 | ||
| + | if tick == 4: | ||
| + | # walk around, with collision detection | ||
| + | tick = 0 | ||
| + | if dir == 4 and get_maze(x + 1, y) == 0: | ||
| + | x += 1 | ||
| + | elif dir == 3 and get_maze(x - 1, y) == 0: | ||
| + | x -= 1 | ||
| + | elif dir == 2 and get_maze(x, y + 1) == 0: | ||
| + | y += 1 | ||
| + | elif dir == 1 and get_maze(x, y - 1) == 0: | ||
| + | y -= 1 | ||
| + | x = min(15, max(0, x)) | ||
| + | y = min(15, max(0, y)) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # draw the maze | ||
| + | draw(x, y, tick) | ||
| + | microbit.sleep(50) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (x == 15 and y == 3) or (x==13 and y==15): | ||
| + | music.play(music.NYAN, pin = pin8) | ||
| + | x = 0 | ||
| + | y = 1 | ||
| + | tick = 0 | ||
| + | main() | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
2019年4月10日 (三) 17:24的最新版本
概述
microbit拓展游戏手柄。拥有丰富的输入按键、双轴游戏摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器。结合microbit可以有多样的玩法,增加microbit编程的趣味性!
技术参数
- 输入电源:3V(2节7号干电池)
- PCI插槽可插入microbit作主控
- 拥有丰富的按键、双轴摇杆、震动马达、无源蜂鸣器
使用教程
| game:bit | 说明 | micro:bit引脚 | Python示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 双轴按键游戏摇杆 | 三路模拟输出,输出值分别对应(X,Y)双轴偏移量和Z轴; 按下的输出模拟量800~850,松开输出模拟量1023 |
X轴->P2 Y轴->P1 Z按键->P0 |
获取x轴偏移量: pin2.read_analog() 获取z按键模拟量: pin0.read_analog() |
| Y/X/B/A按键 | 当Y按下按键输出模拟量0~50, 松开输出模拟量1023 当X按下按键输出模拟量200~250, 松开输出模拟量1023 |
P0 | pin0.read_analog() |
| 「START」按键 | 「START」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_A,功能与microbit的A按键功能相同 | BUTTON_A(P5) | button_a.is_pressed()==True #当「START」按键按下 |
| 「SElECT」按键 | 「SElECT」按键连接microbit的BUTTON_B,功能与microbit的B按键功能相同 | BUTTON_B(P11) | button_b.is_pressed()==True #当「SELECT」按键按下 |
| 震动马达 | 输入高电平,触发震动马达,低电平停止震动 | P16 | pin16.write_digital(1) #震动开启 pin16.write_digital(0) #停止震动 |
| 无源蜂鸣器 | 设置频率或音阶,可发出对应频率的电子声音 | P8 | music.pitch(1000,1000,pin8) #蜂鸣器发出1KHz,持续1秒的声音 |
应用示例
无线遥控器
可利用microbit的无线功能,发送game:bit的按键数据。另外一块microbit接收数据后,作出响应。达到无线遥控的功能。可应用在无线遥控手柄的场景上。
- game:bit & micro:bit发送端程序:
from microbit import *
import radio
def getKeyVal():
key = 0
btVal = pin0.read_analog()
if (btVal < 70):
key = 1 # button Y
elif (btVal < 270 and btVal > 130):
key = 2 # button X
elif (btVal < 470 and btVal > 330):
key = 3 # button B
elif (btVal < 670 and btVal > 530):
key = 4 # button A
elif (btVal < 870 and btVal > 730):
key = 5 # rocker button
if button_a.is_pressed():
key = 6 # button start
if button_b.is_pressed():
key = 7 # button select
return key
radio.config(length=32, queue=3, channel=7, power=0, data_rate=radio.RATE_1MBIT)
radio.on()
while True:
sendBuff = [0,0,0,0,0,0]
tmp = pin2.read_analog() # axix x
sendBuff[0] = tmp & 0xff
sendBuff[1] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff
tmp = pin1.read_analog() # axis y
sendBuff[2] = tmp & 0xff
sendBuff[3] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff
tmp = getKeyVal() # button val
sendBuff[4] = tmp & 0xff
sendBuff[5] = (tmp >> 8) & 0xff
radio.send_bytes(bytearray(sendBuff))
#print(sendBuff)
sleep(50)
- micro:bit接收端程序:
from microbit import *
import radio
radio.config(length=32, queue=3, channel=7, power=0, data_rate=radio.RATE_1MBIT)
radio.on()
while True:
tmp = radio.receive_bytes()
if (tmp != None):
x = (tmp[1]<<8)|tmp[0]
y = (tmp[3]<<8)|tmp[2]
key = (tmp[5]<<8)|tmp[4]
#print(x)
#print(y)
#print(key)
走迷宫
game:bit手柄和micro:bit的led屏互动的小游戏!通过game:bit的摇杆控制来行走迷宫,趣味十足!
gamebit_maze例程下载
- 以下迷宫图,从黄色点启始,蓝色点为出口。也可通过修改maze[]数组,设计自己的迷宫图!
"""
A simple maze program. You are the flashing dot and can walk around
using the accelerometer.
"""
import microbit
from microbit import *
import music
d = microbit.display
# the maze data, as binary numbers (outside walls are added automatically)
maze = [
0b1111111111111111,
0b0011110101001001,
0b1000010101011101,
0b1110110100000000,
0b1100000111110111,
0b1001011101000001,
0b1011010001011101,
0b1010000100000101,
0b1000111111101101,
0b1010110001000111,
0b1010000100010001,
0b1010101111010111,
0b1010101101010001,
0b1010100100011101,
0b1000110111011001,
0b1111111111111011,
]
def getRockerVal():
Dir = 0
val1 = pin1.read_analog()
val2 = pin2.read_analog()
if val1 > 750:
Dir = 1 #up
elif val1 < 250:
Dir = 2 #down
elif val2 < 250:
Dir = 3 #left
elif val2 > 750:
Dir = 4 #right
print(Dir)
return Dir
def get_maze(x, y):
if 0 <= x < 16 and 0 <= y < 16:
return (maze[y] >> (15 - x)) & 1
else:
return 1
def draw(x, y, tick):
img = microbit.Image(5,5)
for j in range(5):
for i in range(5):
img.set_pixel(i, j, get_maze(x + i - 2, y + j - 2)*5)
# draw the player, flashing
img.set_pixel(2, 2, (tick & 1)*4+5)
d.show(img)
def main():
x = 0
y = 1
tick = 0
while True:
dir = getRockerVal()
tick += 1
if tick == 4:
# walk around, with collision detection
tick = 0
if dir == 4 and get_maze(x + 1, y) == 0:
x += 1
elif dir == 3 and get_maze(x - 1, y) == 0:
x -= 1
elif dir == 2 and get_maze(x, y + 1) == 0:
y += 1
elif dir == 1 and get_maze(x, y - 1) == 0:
y -= 1
x = min(15, max(0, x))
y = min(15, max(0, y))
# draw the maze
draw(x, y, tick)
microbit.sleep(50)
if (x == 15 and y == 3) or (x==13 and y==15):
music.play(music.NYAN, pin = pin8)
x = 0
y = 1
tick = 0
main()